Contents
- 1 Hiatal Hernia Treatment Options
- 1.1 Lifestyle Modifications for Hiatal Hernia Management
- 1.2 Dietary Strategies: A Symphony of Food Choices
- 1.3 Taming the Acid Tide
- 1.4 Portion Control: Less is More
- 1.5 Timing is Everything
- 1.6 Weight Management: A Lighter Load for Your Diaphragm
- 1.7 Embracing Exercise: A Path to Wellness
- 1.8 Nutritional Balance: Fueling Your Body
- 1.9 Smoking Cessation: A Breath of Fresh Air
- 1.10 Understanding the Link
- 1.11 Additional Lifestyle Tips: Embracing Holistic Wellness
- 1.12 Medication Considerations: Striking the Right Balance
- 1.13 Surgical Interventions for Hiatal Hernia Repair: When Lifestyle and Medication Aren’t Enough
- 1.14 Understanding When Surgery is Considered
- 1.15 Fundoplication: The Most Common Approach
- 1.16 Laparoscopic Repair: Minimally Invasive Approach
- 1.17 Recovery and Post-Operative Care
- 1.18 Living with Hiatal Hernia: Navigating Long-Term Management and Well-being
- 1.19 Managing Long-Term Symptoms
- 1.20 Preventing Recurrence
Imagine a world without the nagging discomfort of heartburn, the unsettling sensation of food backing up into your esophagus, or the constant fear of indigestion. For millions of people worldwide, this dream is a distant reality, marred by the presence of a hiatal hernia. However, exploring hiatal hernia treatment options offers hope and possibilities for those seeking relief from these persistent symptoms.
A hiatal hernia occurs when a fragment of the stomach protrudes through a weakened opening in the diaphragm. It is the muscle that separates the abdomen from the chest cavity. This misaligned anatomy can lead to a cascade of digestive woes, disrupting your daily life.
If you’re among those struggling with the relentless grip of hiatal hernia symptoms, know that you’re not alone. This condition affects an estimated 5% of the population, and its prevalence increases with age. But there is hope.
Hiatal Hernia Treatment Options
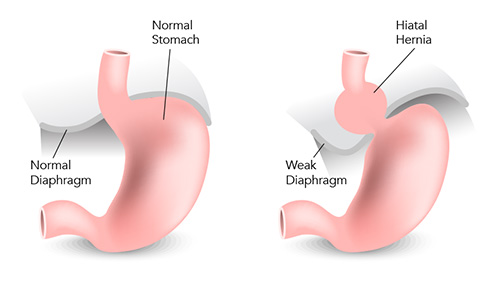
With a comprehensive understanding of hiatal hernia treatment options, you can regain control over your digestive health and reclaim the comfort you deserve. We’ll explore lifestyle modifications that can alleviate symptoms, unravel the science behind medications, and uncover the surgical approaches that can restore anatomical integrity.
Together, we’ll transform your hiatal hernia from an obstacle into an opportunity to reclaim your digestive comfort, rediscover the joy of eating, and embrace a life free from the constraints of digestive distress.
Lifestyle Modifications for Hiatal Hernia Management
Navigating the complexities of hiatal hernia management often requires a multifaceted approach that extends beyond medication. When implemented effectively, lifestyle modifications can play a pivotal role in alleviating symptoms.
Dietary Strategies: A Symphony of Food Choices
The foods we consume profoundly impact our digestive processes, and in the context of hiatal hernia, making informed dietary choices becomes paramount. Embracing a diet that minimizes acid reflux is essential for symptom management.
Taming the Acid Tide
Excess stomach acid is a primary culprit in hiatal hernia-related discomfort. To quell this acidic surge, avoid foods that cause acid production, such as fatty or fried foods, tomato sauce, alcohol, chocolate, mint, garlic, onion, and caffeine. Embracing a low-fat, high-fiber diet can further dampen acid production and promote digestive harmony.
Portion Control: Less is More
Overindulging in large meals can strain the diaphragm and aggravate symptoms. Instead, opt for smaller, more frequent meals during the day to ease the burden on your digestive system. This strategy allows for efficient food breakdown and absorption, minimizing the risk of heartburn and other digestive discomforts.
Timing is Everything
The timing of your meals can significantly influence symptoms. Avoid eating close to bedtime, as lying down with a full stomach can exacerbate acid reflux. Allow adequate time for digestion before retiring for the night, giving your stomach ample time to empty and reducing the likelihood of nocturnal heartburn.
Weight Management: A Lighter Load for Your Diaphragm

Excess weight can exert undue pressure on the diaphragm, contributing to the enlargement of a hiatal hernia. Therefore, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing it. Engage in regular exercise and adopt a balanced diet to attain and sustain a healthy weight.
Embracing Exercise: A Path to Wellness
Regular exercise contributes to weight management and promotes overall digestive health. Aim for at least thirty minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity most days of the week. Engage in activities you enjoy, whether brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
Nutritional Balance: Fueling Your Body
A balanced diet supplies the essential nutrients your body needs to function optimally, including those that support digestive health. Prioritize whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein sources. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated and unhealthy fats.
Smoking Cessation: A Breath of Fresh Air
Smoking is a detrimental habit that exacerbates hiatal hernia symptoms and increases the risk of complications. Quitting smoking improves not only gastrointestinal health but also enhances overall vigor. Seek support from healthcare providers or smoking cessation programs to help you break free from this harmful habit.
Understanding the Link
Smoking weakens the muscles that support the diaphragm, making it more susceptible to damage and contributing to hiatal hernia development. Additionally, smoking increases stomach acid production, further aggravating hiatal hernia symptoms.
Seeking Support
Quitting smoking can be rough, but with support, it is achievable. Consult your healthcare provider for guidance and recommendations on smoking cessation strategies. Consider joining support groups or utilizing online resources to connect with others on the path to quitting smoking.
Additional Lifestyle Tips: Embracing Holistic Wellness
Beyond dietary modifications and weight management, additional lifestyle practices can enhance hiatal hernia management and promote overall digestive health.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Lifting the Head of the Bed): Gravity can play a role in acid reflux, so boosting the head of your bed by four to six inches can help thwart stomach acid from backing up into the esophagus. This can be achieved by using wedge pillows or placing blocks under the legs of the bed at the head end.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Avoid Tight-fitting clothing), particularly around the waist. Tight-fitting clothing can put additional pressure on the diaphragm and worsen the hiatal hernia. Opt for loose-fitting, comfortable clothing to allow for unrestricted breathing and digestion.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Managing Stress): Chronic stress can exacerbate the problem and interfere with digestive processes. Incorporate stress-management techniques into your daily routine, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Engaging in activities that further relaxation can help reduce acid production.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Chewing Thoroughly): Proper chewing is essential for efficient digestion. Take your time to chew your food thoroughly before swallowing it to break it into smaller pieces, reducing the burden on your stomach and minimizing the risk of heartburn.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Avoiding Late-Night Eating): Eating close to bedtime can contribute to acid reflux and disrupt sleep. Allow adequate time for digestion before retiring for the night to promote restful sleep and prevent nighttime heartburn.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Regular Probiotics): Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health and may help alleviate hiatal hernia symptoms. Consider incorporating probiotic supplements or probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, kefir, or fermented vegetables, into your diet.
By implementing these lifestyle modifications, you can actively manage your hiatal hernia and enhance your digestive health. Remember, consistency is critical. Making these changes a regular daily routine can significantly improve your condition.
Medications for Hiatal Hernia Relief
While lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing this condition, medication often becomes necessary to provide additional relief and prevent complications. Understanding the different classes of medications available and their mechanisms of action is crucial for making informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): The Powerhouse of Acid Suppression
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the cornerstone of hiatal hernia medication therapy. They prevent stomach acid production, effectively reducing the volume of acid that can reflux into the esophagus and cause discomfort.
- Mechanism of Action: PPIs target gastric parietal cells, the cells responsible for acid production in the stomach. They bind to an enzyme called H+K+-ATPase, which is essential for acid secretion. By blocking this enzyme, PPIs effectively halt stomach acid production.
- Effectiveness: PPIs are highly effective in reducing stomach acid production and alleviating hiatal hernia symptoms, particularly heartburn. They are typically prescribed for short-term use, but in some cases, long-term therapy may be necessary.
H2 Blockers: An Alternative for Mild Cases
H2 blockers, while less potent than PPIs, offer an alternative medication option for individuals with mild symptoms. They work by blocking histamine receptors, which stimulate acid production in the stomach.
- Mechanism of Action: H2 blockers bind to histamine receptors on gastric parietal cells, preventing histamine from signaling the cells to produce acid. As a result, H2 blockers reduce stomach acid production, but to a lesser extent than PPIs.
- Effectiveness: H2 blockers are generally effective in controlling mild symptoms, particularly daytime heartburn. They may be a suitable option for individuals who cannot tolerate PPIs or prefer a less potent medication.
Antacids: Instant Relief for Heartburn
Antacids provide immediate relief from heartburn by neutralizing stomach acid. They are typically taken over the counter and are considered safe for short-term use.
- Mechanism of Action: Antacids contain substances, such as aluminum hydroxide or calcium carbonate, that neutralize stomach acid. They work quickly to relieve heartburn symptoms but do not address the core cause of acid production.
- Effectiveness: Antacids offer prompt relief from heartburn, particularly after meals or when symptoms are mild. They are not intended for long-term use as they do not address the fundamental cause of acid reflux and may interfere with the absorption of certain medications.
Medication Considerations: Striking the Right Balance
While medications can effectively manage the symptoms, it is crucial to use them appropriately and be aware of likely side effects and interactions.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Adherence): Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding the dosage, timing, and duration of medication use. Taking medications as prescribed is essential for achieving optimal symptom control and minimizing the risk of side effects.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Side Effects): Look for potential side effects of each medication. PPIs, for instance, may cause headaches, diarrhea, and bone loss. H2 blockers may cause constipation, while antacids can lead to diarrhea or rebound acid production.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Interactions): To prevent potential interactions, notify your doctor about all medications, supplements, or herbal remedies you are taking. Some medicines may interfere with the effectiveness or absorption of hiatal hernia medications.
Remember, medications should complement, not replace, lifestyle modifications. Combining medication therapy with dietary changes, weight management, and stress-management techniques can provide comprehensive relief and improve overall digestive health.
Surgical Interventions for Hiatal Hernia Repair: When Lifestyle and Medication Aren’t Enough
In some cases, lifestyle modifications and medication may not provide adequate relief for hiatal hernia. Surgical intervention may offer the best chance for long-term symptom control and improved quality of life for individuals with severe or recurrent symptoms.
Understanding When Surgery is Considered
The decision to undergo surgery for hiatal hernia repair is carefully considered based on several factors, including:
- Severity of Symptoms: Surgery may be necessary if symptoms significantly impact daily life despite lifestyle modifications and medication.
- Recurrence: If hiatal hernia symptoms recur despite adequate treatment, surgery may be recommended to prevent further complications.
- Age and Overall Health: Surgery is generally considered more appropriate for younger, healthier individuals who can tolerate the procedure and recovery process.
Fundoplication: The Most Common Approach
Fundoplication is the most widely used surgical technique for hiatal hernia repair. It involves wrapping the upper portion of the stomach around the esophagus, creating a valve-like mechanism that strengthens the weakened diaphragm and prevents stomach acid from refluxing into the esophagus.
- Types of Fundoplication: There are two main types of fundoplication: Nissen fundoplication and partial fundoplication. Nissen fundoplication is the most common and involves wrapping the entire upper portion of the stomach around the esophagus. Partial fundoplication wraps a smaller portion of the stomach around the esophagus to balance symptom relief with swallowing ease.
- Effectiveness: Fundoplication is highly effective in controlling hiatal hernia symptoms, with success rates of over 90%. It is also considered a durable procedure, with long-term relief in most cases.
Laparoscopic Repair: Minimally Invasive Approach
Laparoscopic repair is a minimally invasive surgical technique for hiatal hernia repair. It involves making small incisions and using specified instruments, reducing pain, scarring, and recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.
- Procedure: During laparoscopic repair, small incisions are made in the abdomen, and a laparoscope, a narrow cylinder with a camera, is inserted. The surgeon utilizes the laparoscope to visualize the internal organs and guide specialized instruments for fundoplication.
- Benefits: Laparoscopic repair offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including reduced pain, scarring, and recovery time. Patients typically experience a shorter hospital stay and a faster return to normal activities.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Following hiatal hernia surgery, a period of recovery and post-operative care is essential. The specific recovery timeline varies depending on the individual and the surgical approach.
- IHiatal hernia treatment options (initial Recovery): Most patients experience some discomfort and fatigue in the days following surgery. Pain medication is typically prescribed to manage discomfort. Patients are encouraged to rest and gradually increase activity levels as tolerated.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Diet): A soft or liquid diet may be recommended for the first few days following surgery to allow the esophagus to heal. As healing progresses, a gradual transition to a regular diet can occur.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Follow-up Visits): Continuous visits with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing and ensure optimal recovery.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Seeking Support): Embarking on the surgical journey can be overwhelming. Seek support from healthcare providers, friends, and family to navigate the process and address any concerns. Support groups, online forums, and communities can provide valuable connections and shared experiences.
While lifestyle modifications, medication, and, in some cases, surgery can provide effective management, living with a hiatal hernia often requires ongoing attention and proactive strategies to maintain symptom control and enhance the quality of life.
Managing Long-Term Symptoms

Individuals with hiatal hernia may experience long-term symptoms, primarily heartburn, even after successful treatment. This happens because the hernia’s underlying structural changes may not be completely reversible. Thus, ongoing management strategies become crucial to minimize symptoms and prevent complications.
- Maintaining Lifestyle Modifications: Adhering to earlier lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, weight management, and stress-management techniques, remains essential for long-term symptom control. These practices help reduce the risk of acid reflux and promote overall digestive health.
- Medication Adherence: If prescribed medication, such as PPIs or H2 blockers, continues to be necessary, it is imperative to take them as directed. Consistent medication use helps maintain symptom control and prevents recurrence.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Regularly monitor symptoms and communicate any shifts or concerns with your healthcare provider. Early identification of worsening symptoms can lead to timely adjustments in treatment plans.
Preventing Recurrence
You can take steps to reduce the likelihood of recurrence, although a hiatal hernia cannot be cured entirely.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Maintaining a Healthy Weight): Excess weight can contribute to hiatal hernia recurrence. Maintaining a healthy weight lowers pressure on the diaphragm and helps prevent the hernia from enlarging.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Avoiding Heavy Lifting): Strenuous activities involving heavy lifting can strain the diaphragm excessively, increasing the risk of recurrence. Avoid lifting heavy objects or engage in alternative forms of exercise that do not strain the diaphragm.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Managing Underlying Medical Conditions): Underlying medical conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), can promote hiatal hernia development and recurrence. Effectively managing these conditions can help reduce the risk of recurrence.
Seeking Support
Living with a hiatal hernia can be challenging, and seeking support can make a substantial difference in your journey.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Communicating with Healthcare Providers): Maintain open communication with your healthcare providers. Discuss your doubts, ask questions, and seek guidance on managing your hiatal hernia effectively.
- Joining Support Groups: Consider joining support groups or online communities that connect individuals with hiatal hernia. Sharing experiences, exchanging tips, and receiving emotional support can be invaluable.
- Hiatal hernia treatment options (Maintain a Positive Outlook): Approach hiatal hernia management with a positive mindset. Focus on your progress, the strategies that work for you, and the support available. A positive outlook can enhance your overall well-being as you navigate the condition.
Remember, hiatal hernia management is an ongoing process that requires dedication and self-care. By understanding the condition, implementing effective strategies, and seeking support, you can empower yourself to manage the situation effectively.
As you embark on the journey of hiatal hernia management, remember that you are not alone. With the knowledge and tools mentioned in this comprehensive guide, you can take control of your digestive health and reclaim the comfort you deserve.
To alleviate symptoms, embrace the power of lifestyle adjustments, such as dietary changes, weight management, and stress-reduction techniques. Understand the role of medications, such as PPIs, H2 blockers, and antacids, in effectively relieving and managing hiatal hernia. Explore the options for surgical intervention, such as fundoplication and laparoscopic repair, when lifestyle and medication are not enough.
Remember, hiatal hernia management is a journey, not a destination. Be patient with yourself, celebrate your progress, and seek support whenever needed. By taking charge of your health and employing the strategies in this guide, you can confidently navigate hiatal hernia and reclaim the digestive comfort you deserve.
DISCLAIMER: All content on this website is presented solely for educational and informational objectives. Do not rely on the information provided as a replacement for advice, diagnosis, or treatment from a qualified medical expert. If you are pregnant, nursing, or have any preexisting medical concerns, talk to your doctor before using any herbal or natural medicines.
References
- Cleveland Clinic: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8098-hiatal-hernia
- https://www.health.com/hiatal-hernia-treatment-8302968
- Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gerd/expert-answers/heartburn-gerd/faq-20057894
- Hopkins Medicine: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hernias/hiatal-hernia
- Verywell Health: https://www.verywellhealth.com/treating-hiatal-hernias-1742603
- WebMD: https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/hiatal-hernia

