Contents
Type II diabetes is a condition where levels of blood glucose in the body are too high. Many seniors have friends who have already been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, so they may worry that they could be someone who is diagnosed next!
It is a chronic condition that can happen to anyone of any age, but people aged 65 years and above appear to have the highest prevalence of diabetes compared to any other age group. Senior citizens are more at risk of getting the disease if they lead a sedentary lifestyle, have a family history of diabetes, eat an unhealthy diet, or are overweight.
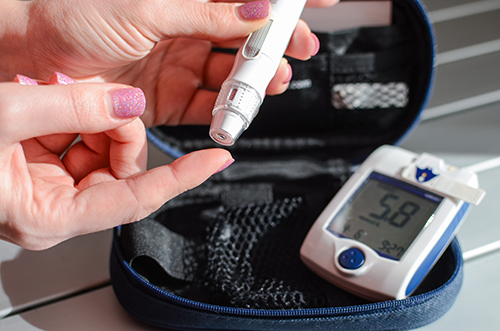
How Does Type II Diabetes Start?
Our body turns most of the food we eat into glucose, which gives our body the energy to function optimally. A hormone, insulin, made by the pancreas, is also needed to turn glucose into energy.
Insulin’s primary function is to help glucose enter our cells to supply the body with energy. However, in some cases, the body might not be able to make enough insulin, or the body’s response to insulin may not function optimally. Therefore, there is too much blood glucose in the system. This is how diabetes develops. Over time, too much causes a variety of health problems.
Every case of diabetes should be taken seriously and adequately managed to sustain a longer, healthier life. A diagnosis of this disease should never be taken lightly.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is when an individual’s glucose levels in the bloodstream are higher than average but aren’t at the same level as someone diagnosed with diabetes. If a person is in this stage, it can still be reversed if they take steps to make the lifestyle changes required. Prediabetes also predisposes an individual to stroke and heart attack, so it is a definite warning sign to make changes fast.
Signs and Symptoms of Type II Diabetes
Some signs of type 2 diabetes include tiredness, vision troubles such as blurred vision, frequent urination, increased hunger and thirst, wounds healing slowly, and skin infections.
In some cases, symptoms of type II diabetes can develop very slowly and be hardly noticed. Many senior-aged people assume these symptoms are part of growing old, such as when their skin cuts and the wounds don’t heal as fast as they used to. They may be an indicator of a more serious health problem.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Type II Diabetes
To be able to treat diabetes, it has to be diagnosed by a doctor. Diabetes needs proper care and treatment. Ensure you see a doctor if you experience any of the abovementioned signs and symptoms, especially if you are an at-risk senior citizen. To make a proper diagnosis, doctors conduct several blood tests.
- A1C Test: This test shows your average glucose levels over the past three months. It can be given at any time during the day.
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test – This test necessitates the patient fasting for at least 8 hours.
- Random Plasma Glucose Test – This test can be conducted anytime during the day.
Treating diabetes involves long-term care for the person diagnosed with the disease. Some people with type II diabetes can monitor their condition and symptoms by simply living a healthier lifestyle where diet and exercise are a primary focus. Other people may need medications and insulin injections to manage their condition. Over time, people with diabetes need to integrate lifestyle changes and medications.

Most diabetes management plans will include ways to track glucose levels, make healthier food choices, and methods to get active.
Diabetes might be a chronic health condition, but it is possible to get and stay healthy with proper management. For older people, regular check-ups and assessments will be beneficial in managing the disease. Any changes or updates in a person’s health status, such as adding a new health complication, will likely lead to changes in their diabetes management plan.
As with any disease, prevention is better than cure. So the best way to not be concerned about having to live with diabetes is not to get it at all! Start eating healthy and start exercising. A sedentary lifestyle will not help you at all.
DISCLAIMER: All content on this website is presented solely for educational and informational objectives. Do not rely on the information provided as a replacement for advice, diagnosis, or treatment from a qualified medical expert. If you are pregnant, nursing, or have any preexisting medical concerns, talk to your doctor before using any herbal or natural medicines.
References
- Diabetes in Older People: https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/diabetes/diabetes-older-people
- Prediabetes: https://www.diabetes.org/a1c/diagnosis
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2023: https://diabetesjournals.org/care/issue/46/Supplement_1
- Type 2 diabetes – Symptoms and causes: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20351193
- Symptoms & Causes of Diabetes: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/symptoms-causes
