Contents

All fiber-rich foods are exclusively plant-based. Plant-based foods all contain some fiber in their natural state, particularly whole grains (unrefined) and legumes.

According to the American Dietetic Association, the daily average value of fiber-rich foods for adults is 25 grams (between 20 and 35 g). To achieve this amount is not a problem with a plant-based diet. However, this is not the case in diets primarily based on animal products.
You can determine the minimum amount of daily fiber via fiber-rich foods for children over three years old by adding five to their age in years (+5). For example, the amount would be 15 grams for a ten-year-old child.
Chemical Composition and Description of Fiber
Dietetic fiber is formed by various substances such as cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, gums, mucilage, and other polysaccharides sharing the following characteristics:
- They are of plant origin.
- They are generally found in the plant’s cell walls, although some fiber types, such as gums and mucilage, are found in the cellular cytoplasm.
- They are indigestible in the small intestine. Some are partially digested by bacteria in the colon, causing flatulence.
Function

- It reduces the risk of constipation and accompanying disorders, such as colon diverticulosis, colon cancer, and hemorrhoids. This protective effect is mainly performed by insoluble fiber.
- It contributes to the avoidance of excess cholesterol, particularly soluble fiber.
- It is an emollient and protects the intestinal mucosa, particularly soluble fiber.
- It improves diabetes.
Fiber deficiency symptoms include constipation, diverticulosis, arteriosclerosis, and greater cancer risk.
Too much fiber can reduce the absorption of iron, zinc, and other minerals. Excessive insoluble fiber can irritate the intestine, producing colitis.
Loss during the processing of foods: refined grains lose as much as 95% of their fiber.
Fiber-Rich Foods List
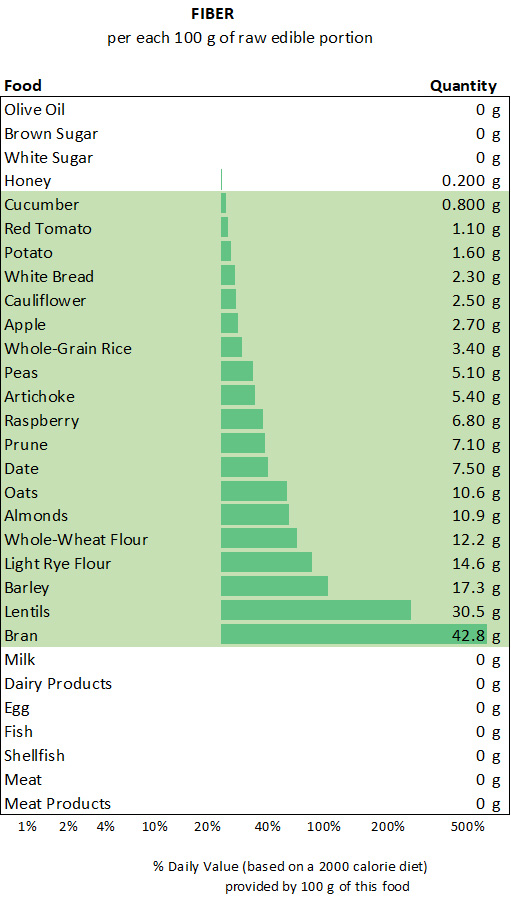
Dietary fiber is found exclusively in plant-based foods. These foods contain some fiber, particularly whole grains (unrefined) and legumes in their natural state.
DISCLAIMER: All content on this website is presented solely for educational and informational objectives. You should not rely on the information provided as a replacement for advice, diagnosis, or treatment from a qualified medical expert. If you are pregnant, nursing, or have any preexisting medical concerns, you should talk to your doctor before using any herbal or natural medicines.
REFERENCES
- George D. Pamplona-Roger, M.D. “Encyclopedia of Foods and Their Healing Power.” George D. Pamplona-Roger, M.D. Encyclopedia of Foods and Their Healing Power. Trans. Annette Melgosa. Vol. 1. Chai Wan: Editorial Safeliz, 2005. 388. Print. [fiber-rich foods]
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: “Fiber: Essential for a Healthy Diet”
- American Heart Association: “Fiber and Heart Health”
- Harvard Health Publishing: “Fiber: A diet must-have for good health”
- Mayo Clinic: “Dietary fiber: Essential for a healthy diet”
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: “Fiber”
- The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: “Dietary fiber and risk factors for cardiovascular disease and diabetes”
- The Journal of Nutrition: “Dietary fiber and prebiotics in the prevention of colorectal cancer”
- The Fiber Optic Association: “Fiber FAQs” (used to ensure the terminology for different fiber types was consistent across both dietary and optical fiber references)
